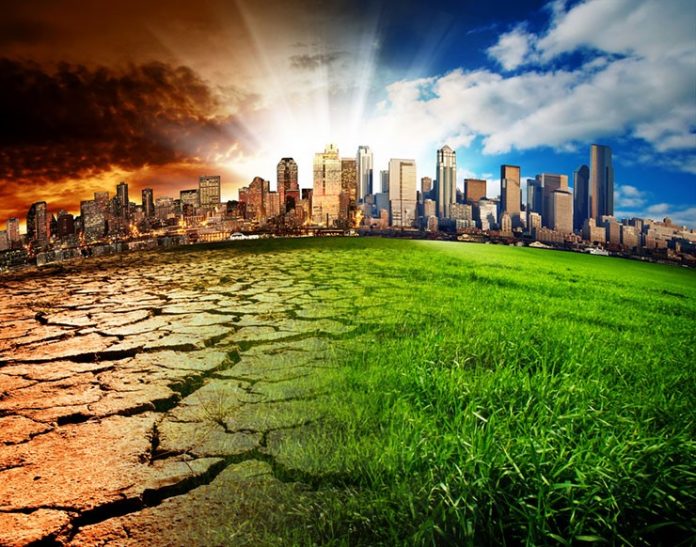
With the world population expected to grow to 8.1billion come 2030 at an annual increase of 75 million people, the conventional food systems are undoubtedly threatened amidst the effects of climate change. Approximately 42% of the crop productivity has been compromised by diseases, weeds, a reduction in the amount of arable land, and crop varieties are nearing their biological and physical limits of productivity.
Under these climate and socio-economic changes investing in sustainable food supply and nutritionally balanced and diverse diets can help adapt food systems to the changing world. Plant biotechnology presents a promising tool, with remedies that can contribute to sustainable gains in agricultural productivity, poverty reduction and food security.

Post-harvest loss control
Food security is negatively affected by post-harvest losses, with the losses amounting to 30 % of that harvest yields. The presence of toxicogenic and spoilage micro-organisms induces microbial activities that lead to spoilage. But produce shelf life can now be boosted thanks to genetic engineering. Plant components that cause early deterioration, can be removed by incorporating an antisense gene to significantly reduce the enzymes that induce ripening. A large amount of yield goes to waste at harvest especially in slaughter harvesting, where robotic harvests both immature and mature, ripe and unripe yields.A

Cloning of plants can help realize uniform characteristics, same growth rate and ripening time. This helps ensure an even harvest, thus reducing wastage.
Also by Author: Green Economy: A Cornerstone to Sustainable Development
Increased yields
The goal of every farmer is to increase on yield at any given season. This has however been threatened by emerging pest and diseases. But all is not lost scientist can now develop pest and disease-resistant crops varieties by incorporating proteins that provide plants with the ability to protect themselves from fungal, viral, or bacterial diseases. Bt rice and Bt corn have revolutionized pest control and most farmers have benefited, with increased productivity.
Desirable qualities can also be incorporated into crops such includes, increasing flowering capacity, photosynthesis and stress resistance-to acidity and salinity. This position plants for better performance.

Through tissue culture, disease-free planting materials can be produced. Seed materials can be accessed throughout the year, with no season cycle restriction.
Competitive advantage
Competitive effect of weeds can also be minimized by developing herbicides resistant crop varieties. This would imply reduce the need for agrochemicals thus minimal residues in the final products. Biotech has also facilitated mass production of biological weapons with insecticidal effects- Such biological weapons like fungi can control other fungi, attack weeds, pests, and harmful insects. They are more environmentally friendly and less expensive nature presents an additional advantage compared to agrochemicals.
Value addition to Nutritionally balanced diets
The food production will not only demand to feed more people but also emphasize adding value to the products. Molecular biology and gene technology offer a great opportunity for value addition in the cereal sector and other food products for increased nutritional content. Thanks to biotech the protein content of cassava and rice can be increased to ensure a well-balanced diet to millions of people that rely on them as staple foods. Likewise, undesirable food components, such as major allergens can now be successfully eliminated by modifying their amino acids sequences.
Revegetation of denuded regions
With increasing desertification associated with deforestation, overgrazing, and fires, biotech crops can be successfully used for ecological restoration. Fast-growing crops can help restore plant cover, that can be utilized as food or feed. Also, the development of drought-resistant varieties has enabled crop production in previously non-arable land.
Scientific evidence present biotechnology as a crucial tool among a range of technologies and can increase food production and be of benefit to the environment. With the population pressure and factor of reducing arable land, biotech can help mitigate agricultural challenges and adapt farming systems in the adverse climate and weather changes.
Women make up a larger percentage of farmers in developing countries, by adopting herbicides tolerant crops and crops with less labor to harvest, they stand less burdened in farm work, and can engage in other economic activities.
Despite the great potential, the technology faces acceptability barriers that hinder its application in agriculture, either due to fear of international competition or loss of vibrant landraces. Nevertheless, its real benefits are indisputable and are a great means of food security.